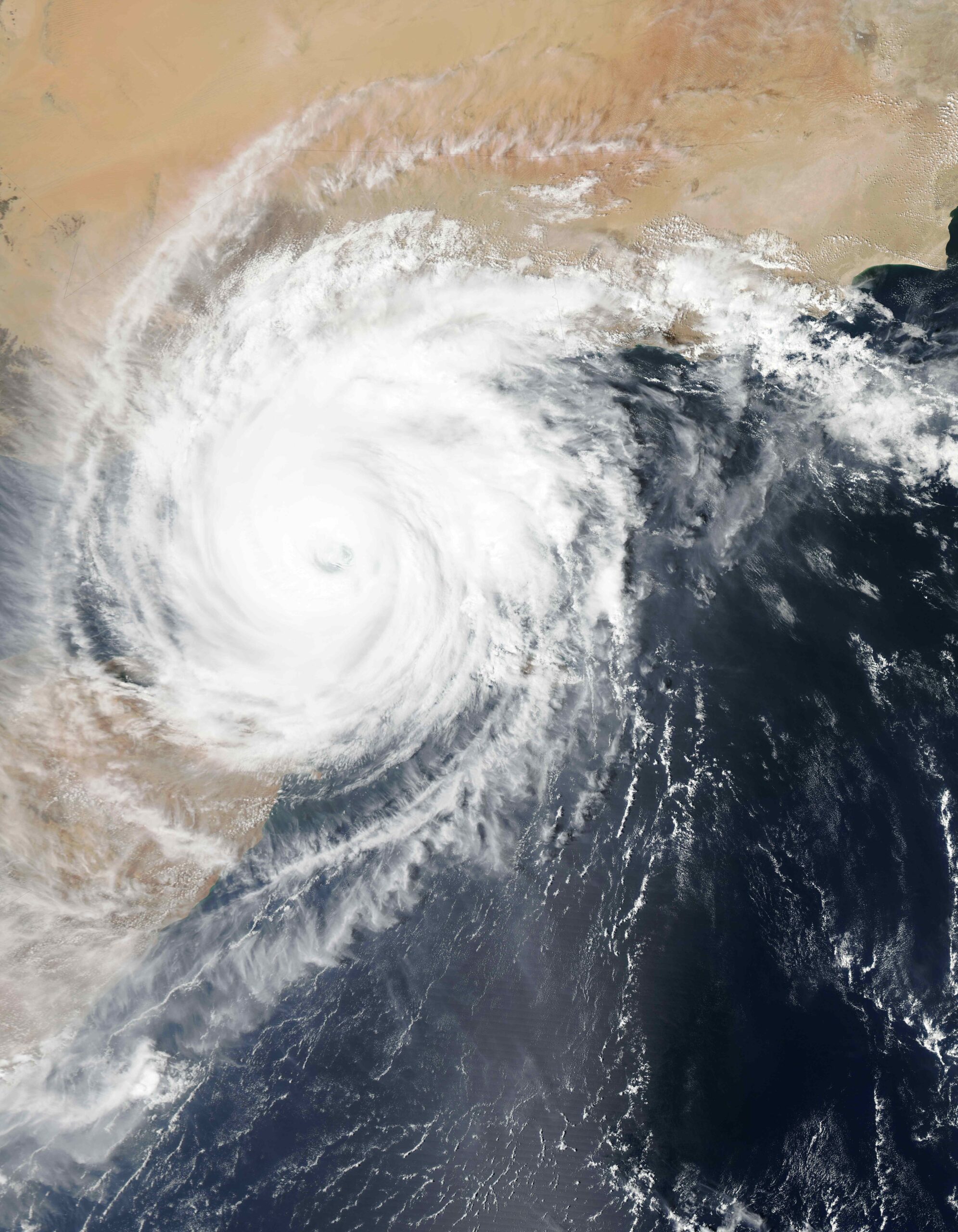
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure center, strong winds, and heavy rain. It has thunderstorms arranged in a spiral pattern and occurs over tropical or subtropical waters, with a counterclockwise rotation in the Northern Hemisphere.
These cyclones are characterized by their closed low-level circulation.
1. Understanding Tropical Cyclones
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. It originates over tropical or subtropical waters and has a closed low-level circulation. Tropical cyclones rotate counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere.
Definition Of A Tropical Cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rotating, organized system of clouds and thunderstorms that originates over tropical or subtropical waters and has a closed low-level circulation.
Characteristics Of A Tropical Cyclone
– Rapidly rotating storm system
– Low-pressure center
– Closed low-level atmospheric circulation
– Strong winds
– Spiral arrangement of thunderstorms
– Heavy rain and squalls
Conditions That Foster Tropical Cyclone Formation
Tropical cyclones form under specific conditions, which include:
- Warm ocean waters
- Moist atmosphere
- Coriolis force
- Low vertical wind shear
These conditions provide the necessary fuel for tropical cyclone development and intensification.
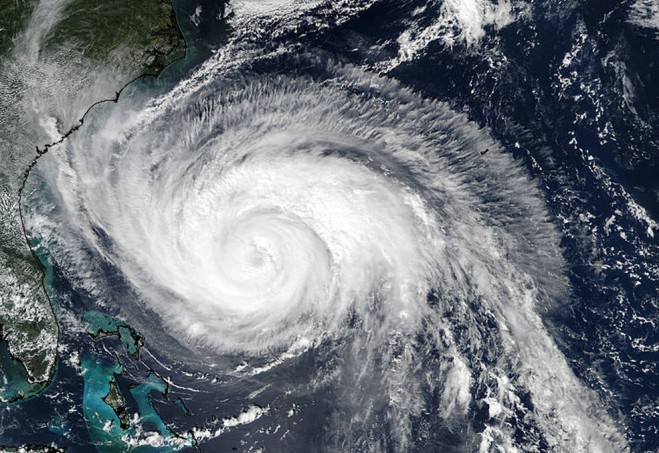

Credit: sensorsandsystems
2. Types Of Tropical Cyclones
A tropical cyclone is a powerful storm system that forms over warm tropical or subtropical waters. It is characterized by strong winds, heavy rain, and a low-pressure center, causing destructive impacts.
3. Impacts Of Tropical Cyclones
Tropical cyclones, also known as hurricanes or typhoons depending on the region, have significant environmental impacts. The strong winds and heavy rains associated with these storms can cause widespread flooding, leading to soil erosion and land degradation. The storm surge, which is a rise in sea level caused by the cyclone, can result in coastal erosion and destruction of habitats, such as coral reefs and mangroves. Additionally, the intense rain can cause water contamination and negatively affect water quality, leading to the spread of waterborne diseases.
The societal impacts of tropical cyclones can be devastating. These storms often result in the displacement of communities, loss of homes, and disruption of essential services such as electricity, water, and transportation. The strong winds can cause extensive damage to infrastructure, including buildings and roads. The impact on communities can also be psychological, as individuals and families may experience trauma and emotional distress due to the loss of loved ones and the destruction of their livelihoods and possessions.
Tropical cyclones have significant economic impacts, causing billions of dollars in damage each year. The destruction of infrastructure, homes, and businesses can lead to costly rebuilding efforts. Additionally, there is often a temporary or prolonged interruption of economic activities, such as agriculture, tourism, and manufacturing. The loss of crops, livestock, and fisheries can result in food shortages and price increases in affected regions. The tourism industry, which is often an important source of revenue for coastal areas, can suffer due to the damage caused by the cyclone and the subsequent decline in visitor numbers.
Throughout history, there have been numerous notable tropical cyclones that have caused significant devastation. Examples include Hurricane Katrina in 2005, which resulted in more than 1,200 deaths and caused over $100 billion in damage in the United States, particularly in New Orleans. In 2013, Super Typhoon Haiyan devastated the Philippines, causing widespread destruction and resulting in thousands of deaths. These case studies highlight the immense power and destructive potential of tropical cyclones, underscoring the need for preparedness and effective response strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions Of Tropical Cyclone
What Is A Tropical Cyclone Vs Hurricane?
A tropical cyclone is a strong storm system with low-pressure center, strong winds, and heavy rain. It rotates counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and forms over tropical or subtropical waters. A hurricane is a type of tropical cyclone that forms in the Atlantic Ocean or eastern Pacific Ocean.
What Is The Definition Of A Tropical Cyclone?
A tropical cyclone is a rotating storm system with low-pressure center and strong winds, producing heavy rain and thunderstorms. It forms over tropical or subtropical waters and has a closed low-level circulation.
Is Tropical Cyclone A Tornado?
A tropical cyclone is not the same as a tornado. A tropical cyclone is a rotating storm system with low pressure, strong winds, and heavy rain, while a tornado is a violent, localized, and narrow storm with a rapidly rotating column of air.
Is A Tropical Cyclone Stronger Than A Hurricane?
A tropical cyclone and a hurricane are the same types of storms, with a low-pressure center, strong winds, and heavy rain. There is no difference in strength between the two.
Conclusion
Tropical cyclones are powerful storms characterized by low-pressure centers, strong winds, and heavy rain. These storms can cause significant damage and destruction in their path. Understanding the characteristics, conditions, and types of tropical cyclones is crucial for preparedness and response efforts.
Whether it’s a hurricane, typhoon, or cyclone, these storms can have devastating impacts on communities. By staying informed and taking necessary precautions, we can minimize the risks and protect ourselves from the wrath of tropical cyclones.